How does modified capitalism differ from pure capitalism? This question delves into the intriguing realm of economic systems, where the interplay of government intervention, social welfare, and market regulation shapes the economic landscape.
Modified capitalism, a distinct variant of pure capitalism, introduces modifications to address societal concerns and promote economic stability. This essay explores the defining characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of modified capitalism, examining its historical evolution and potential future trajectory.
Characteristics of Modified Capitalism
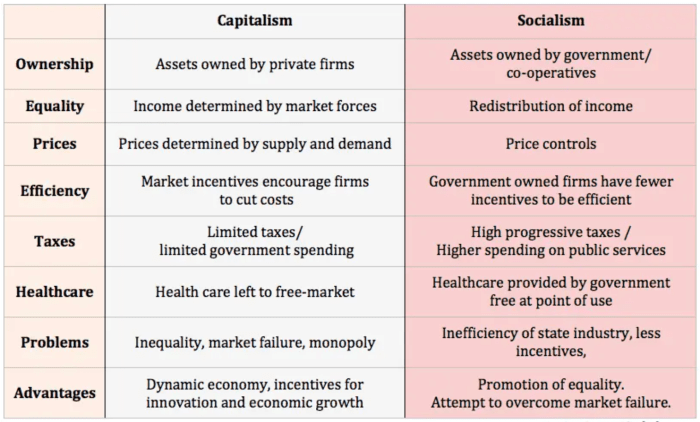
Modified capitalism, also known as social capitalism or welfare capitalism, is a hybrid economic system that combines elements of pure capitalism with government intervention and social welfare programs. It differs from pure capitalism in several key ways:
Government Intervention, How does modified capitalism differ from pure capitalism
Modified capitalism allows for a greater role for government in the economy. Governments may intervene to regulate markets, provide social welfare programs, and redistribute income.
Social Welfare Programs
Modified capitalism typically includes social welfare programs such as healthcare, education, and unemployment benefits. These programs are designed to provide a safety net for those who are unable to fully participate in the market economy.
Regulation of Markets
Modified capitalism often involves government regulation of markets. This regulation can take many forms, such as antitrust laws, environmental regulations, and consumer protection laws.
Advantages of Modified Capitalism
Modified capitalism offers several potential benefits, including:
Reduced Economic Inequality
Government intervention and social welfare programs can help to reduce economic inequality by providing a safety net for the poor and vulnerable.
Improved Social Mobility
Social welfare programs can also improve social mobility by providing opportunities for education, healthcare, and other services that can help people move up the economic ladder.
Increased Economic Stability
Government regulation of markets can help to prevent economic crises by ensuring that markets are functioning efficiently and fairly.
Disadvantages of Modified Capitalism: How Does Modified Capitalism Differ From Pure Capitalism

Modified capitalism also has some potential drawbacks, including:
Reduced Economic Efficiency
Government intervention and regulation can sometimes reduce economic efficiency by creating barriers to entry and stifling innovation.
Increased Government Bureaucracy
Modified capitalism often requires a large government bureaucracy to administer social welfare programs and regulate markets. This can be costly and inefficient.
Stifling of Innovation
Government regulation can sometimes stifle innovation by making it more difficult for new businesses to enter the market and for existing businesses to expand.
Examples of Modified Capitalism
Many countries around the world have implemented modified capitalism. Some examples include:
Nordic Countries
The Nordic countries, such as Sweden and Denmark, have highly developed social welfare systems and a strong role for government in the economy.
Germany
Germany has a social market economy that combines free markets with social welfare programs and government regulation.
Japan
Japan has a modified capitalist system that includes a strong role for government in industrial policy and a high level of social welfare spending.
Historical Development of Modified Capitalism

Modified capitalism has evolved over time in response to changing economic and social conditions.
Early 20th Century
The early 20th century saw the rise of social welfare programs in many countries in response to the growing industrial economy and the resulting social problems.
Post-World War II Era
After World War II, many countries adopted modified capitalist systems as a way to rebuild their economies and promote social stability.
Neoliberal Era
The neoliberal era of the 1980s and 1990s saw a decline in government intervention and social welfare spending in many countries.
21st Century
In the 21st century, there has been a renewed interest in modified capitalism as a way to address the challenges of globalization and inequality.
FAQ Corner
What is the primary difference between modified capitalism and pure capitalism?
Modified capitalism incorporates government intervention, social welfare programs, and market regulation, while pure capitalism advocates for minimal government involvement and free market principles.
What are the potential benefits of modified capitalism?
Modified capitalism can reduce economic inequality, improve social mobility, and enhance economic stability.
What are the potential drawbacks of modified capitalism?
Modified capitalism may lead to reduced economic efficiency, increased government bureaucracy, and stifled innovation.