Cell organelles structures and functions organizer – Delving into the realm of cell organelles, this organizer unveils the intricate structures and diverse functions that orchestrate the symphony of life within the microscopic realm. Embark on a journey to decipher the enigmatic world of these cellular building blocks, their intricate interplay, and their profound impact on cellular health and disease.
As we delve deeper into the topic, we will explore the evolutionary origins of organelles, unravel the mysteries of organelle dysfunction, and witness the cutting-edge advancements in organelle research. This comprehensive guide empowers you with a profound understanding of the fundamental components that govern cellular life, paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries in the future of medicine and biology.
Cell Organelles: Structures and Functions: Cell Organelles Structures And Functions Organizer
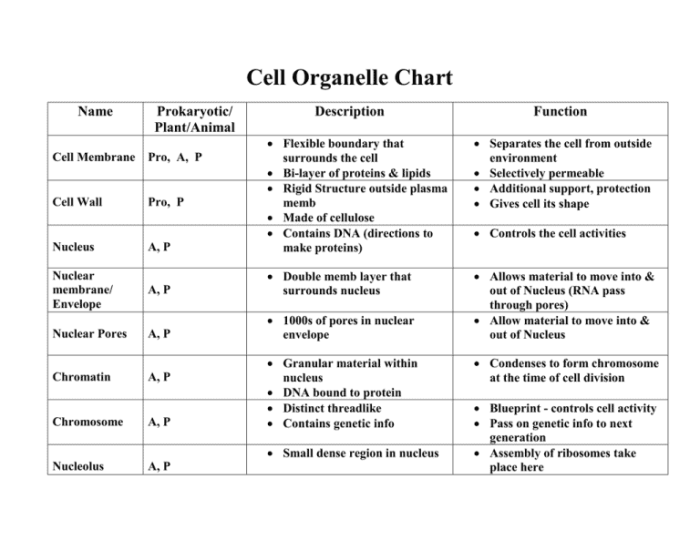
Cell organelles are specialized structures found within eukaryotic cells that perform specific functions essential for cellular life. These organelles are analogous to the organs in our bodies, each with a distinct structure and a unique role in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Various types of cell organelles exist, including the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, peroxisomes, and ribosomes. Each organelle possesses a unique structure that enables it to carry out its specific functions.
Organelle Functions
Cell organelles perform a diverse range of functions that are crucial for cellular survival and proper functioning. These functions include energy production, protein synthesis, waste removal, and cellular communication.
- Mitochondria:Generate energy in the form of ATP through cellular respiration.
- Ribosomes:Synthesize proteins based on the instructions encoded in mRNA.
- Lysosomes:Digest and recycle cellular waste products.
- Golgi apparatus:Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for secretion or storage.
- Endoplasmic reticulum:Synthesizes lipids and proteins, and transports them within the cell.
Organelle Interactions
Cell organelles do not operate in isolation but rather interact and cooperate to maintain cellular homeostasis. These interactions are essential for the efficient functioning of the cell.
For example, the endoplasmic reticulum synthesizes proteins that are then modified and packaged by the Golgi apparatus. These proteins are then transported to the cell membrane or secreted from the cell.
Organelle Evolution
The origins of cell organelles are a subject of ongoing research. The endosymbiotic theory proposes that some organelles, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts, evolved from free-living bacteria that were engulfed by a larger cell.
Evidence supporting this theory includes the presence of their own DNA and the similarity of their ribosomes to those found in bacteria.
Organelle Dysfunction
Dysfunction of cell organelles can lead to a variety of diseases and disorders. For example, mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Lysosomal dysfunction can lead to lysosomal storage diseases, which are characterized by the accumulation of undigested material within cells.
Organelle Research
Research on cell organelles is ongoing, with advancements in microscopy and molecular biology techniques providing new insights into their structure and function.
This research has implications for understanding cellular biology and developing treatments for diseases associated with organelle dysfunction.
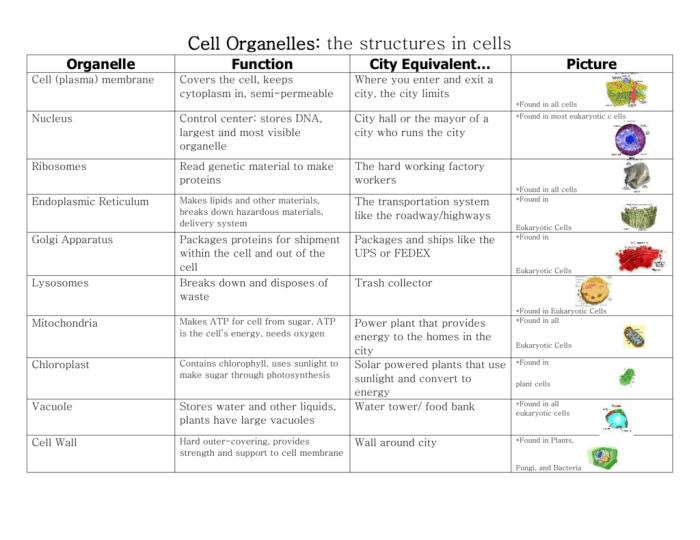
Visual Representation (HTML Table)
The following table summarizes the key cell organelles, their structures, and functions:
| Organelle | Structure | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Double membrane-bound organelle containing the cell’s genetic material | Controls cellular activities and stores genetic information |
| Mitochondria | Double membrane-bound organelle with a folded inner membrane | Produces energy through cellular respiration |
| Endoplasmic reticulum | Network of interconnected membranes | Synthesizes lipids and proteins |
| Golgi apparatus | Stack of flattened membranes | Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins |
| Lysosomes | Membrane-bound organelles containing digestive enzymes | Digest and recycle cellular waste products |
Examples of Organelle Functions
- Mitochondria produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
- Ribosomes synthesize proteins, which are essential for cellular structure and function.
- Lysosomes digest and recycle cellular waste products, preventing their accumulation.
- The Golgi apparatus modifies and packages proteins for secretion or storage.
- The endoplasmic reticulum synthesizes lipids and proteins, and transports them within the cell.
Methods for Studying Organelles
Various methods are used to study the structure and function of cell organelles, including:
- Light microscopy:Uses visible light to visualize organelles.
- Electron microscopy:Uses a beam of electrons to visualize organelles at a higher resolution.
- Immunohistochemistry:Uses antibodies to label and visualize specific organelles.
Procedures for Organelle Isolation, Cell organelles structures and functions organizer
Organelle isolation involves separating specific organelles from the rest of the cell. This can be achieved through a series of steps, including:
- Cell homogenization:Breaking open the cell to release its contents.
- Centrifugation:Separating organelles based on their size and density.
- Immunoaffinity purification:Using antibodies to capture specific organelles.
FAQ Guide
What is the primary function of mitochondria?
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, responsible for generating the majority of the cell’s energy through cellular respiration.
How do ribosomes contribute to protein synthesis?
Ribosomes are the protein synthesis machinery of the cell, responsible for translating genetic information into functional proteins.
What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in cellular secretion?
The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion from the cell.