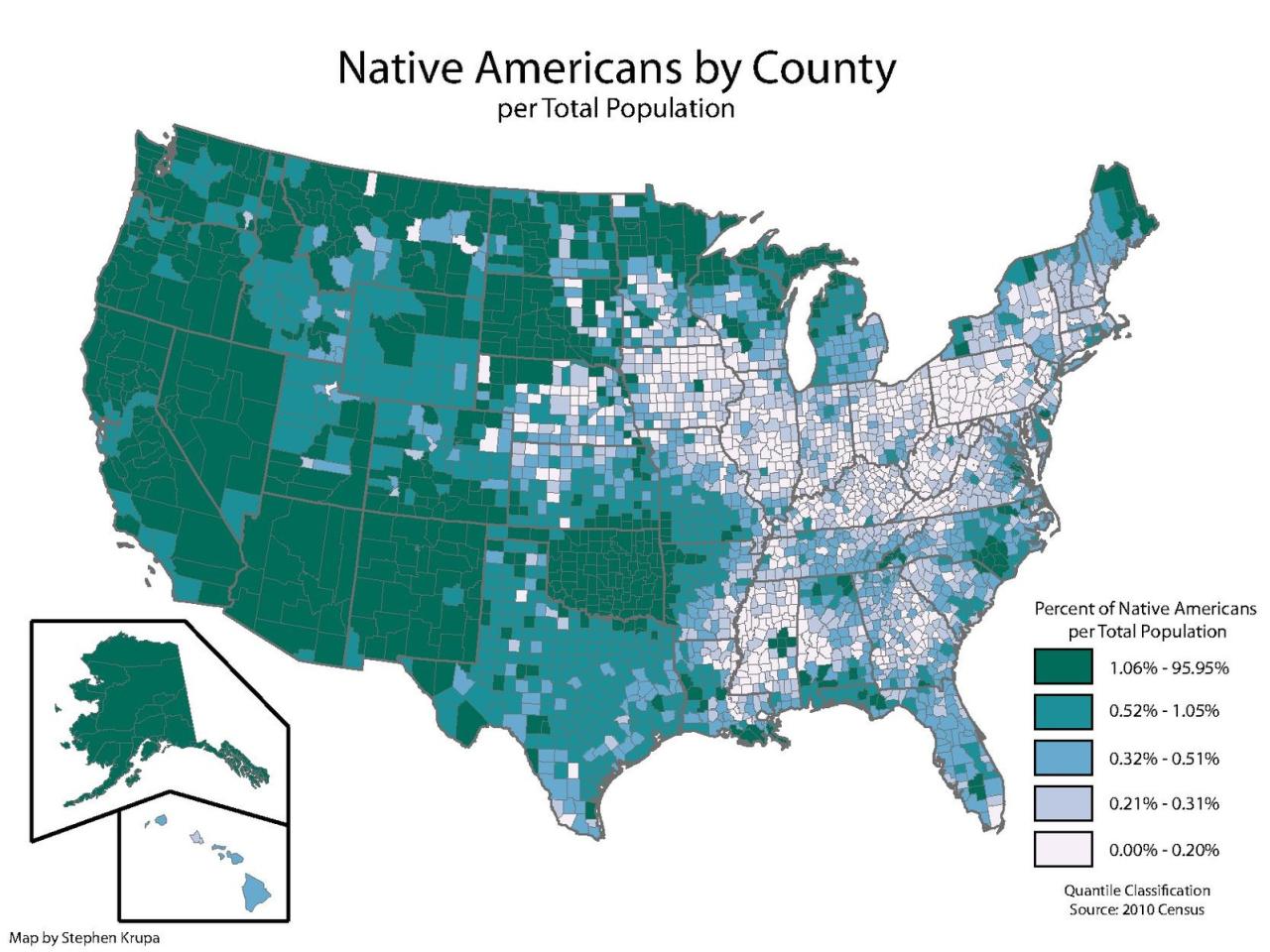
Survey data definition ap human geography – Survey data definition in AP Human Geography encompasses the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of data from a sample of individuals to gain insights into a population’s characteristics, opinions, and behaviors. This invaluable tool enables researchers to gather quantitative and qualitative data, providing a foundation for understanding various geographical phenomena and human experiences.
Survey research plays a crucial role in human geography, offering researchers a means to explore diverse topics such as population dynamics, migration patterns, land use changes, and the impact of environmental factors on human well-being. By employing rigorous sampling techniques and analytical methods, researchers can draw meaningful conclusions and contribute to the advancement of geographical knowledge.
Definition of Survey Data: Survey Data Definition Ap Human Geography
Survey data is a type of research data collected by administering surveys to a sample of individuals. Surveys are questionnaires that ask respondents to provide information about their attitudes, opinions, behaviors, and experiences. Survey data is widely used in human geography to gather information about human populations and their interactions with the environment.
There are two main types of survey data: quantitative data and qualitative data. Quantitative data is numerical data that can be statistically analyzed, while qualitative data is non-numerical data that provides insights into the subjective experiences and perspectives of respondents.
Methods of Survey Data Collection
There are various methods used to collect survey data, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Questionnaires:Self-administered surveys that respondents complete on their own. They are relatively inexpensive and easy to administer, but response rates can be low.
- Interviews:Face-to-face or telephone conversations between a researcher and a respondent. They allow for more in-depth questioning, but they can be time-consuming and expensive.
- Focus groups:Group discussions moderated by a researcher. They provide insights into group dynamics and shared perspectives, but they can be difficult to organize and may not be representative of the wider population.
Sampling Techniques
Sampling techniques are used to select a representative sample of the population of interest. This is important to ensure that the survey results are generalizable to the wider population.
There are different sampling methods, including:
- Random sampling:Each individual in the population has an equal chance of being selected.
- Stratified sampling:The population is divided into subgroups (strata) based on certain characteristics, and then a random sample is selected from each stratum.
- Cluster sampling:The population is divided into clusters (e.g., neighborhoods), and then a random sample of clusters is selected, and all individuals within those clusters are surveyed.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Survey data can be analyzed using a variety of statistical methods, including:
- Descriptive statistics:Summarize the data and provide basic information about the respondents.
- Inferential statistics:Allow researchers to make inferences about the wider population based on the sample data.
- Qualitative analysis:Used to analyze non-numerical data, such as open-ended responses or focus group discussions.
It is important to interpret survey results carefully, taking into account the limitations of the data and the sampling method used.
Ethical Considerations
Survey research involves ethical considerations, such as:
- Informed consent:Respondents must be informed about the purpose of the survey and their rights before participating.
- Confidentiality:Respondents’ identities and responses must be kept confidential.
- Bias:Researchers must minimize bias in the design and administration of the survey.
Applications of Survey Data in Human Geography, Survey data definition ap human geography
Survey data is widely used in human geography research to study a variety of topics, including:
- Population characteristics:Age, gender, education, income, and other demographic characteristics.
- Migration patterns:Reasons for moving, destination choices, and experiences of migrants.
- Health and well-being:Access to healthcare, health behaviors, and quality of life.
- Environmental perceptions and behaviors:Attitudes towards environmental issues, conservation practices, and climate change.
Survey data provides valuable insights into the human dimensions of geography and helps researchers understand the interactions between humans and their environment.
Top FAQs
What is the purpose of survey data in AP Human Geography?
Survey data in AP Human Geography provides researchers with insights into the characteristics, opinions, and behaviors of human populations, aiding in the understanding of geographical phenomena and human experiences.
What are the different types of survey data?
Survey data can be quantitative (numerical) or qualitative (non-numerical), allowing researchers to collect both objective and subjective information from respondents.
How are survey samples selected?
Sampling techniques such as random sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling are employed to ensure that the sample represents the target population accurately.
What methods are used to analyze survey data?
Descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and qualitative analysis are used to analyze survey data, enabling researchers to summarize, interpret, and draw conclusions from the collected data.
What are the ethical considerations in survey research?
Informed consent, confidentiality, and minimizing bias are key ethical considerations in survey research, ensuring the rights and privacy of respondents are protected.